THE 2026-2027 APHELIC APPARITION OF MARS
By: Jeffrey D. Beish
(25-OCT-2020)
INTRODUCTION
Mars appears more Earth-like to us than most of the other planets because we can observe its surface, atmospheric clouds and hazes, and its brilliant white polar caps. The latter are composed of frozen CO2 and underlying water ice, and wax and wane during the Martian year. These aspects, along with the changing seasons and the possibility of life, have made Mars one of the most studied planets in our solar system.
The Red Planet Mars offers both casual and serious observers many challenges and delights, as well as providing astronomers a laboratory to study another planet’s atmosphere and surface. Some Martian features even appear to shift position around the surface over extended periods of time. There are several cooperating international Mars observing programs under way to assist both professional and amateur astronomers. These include the International Mars Patrol (I.M.P.) coordinated by the Mars Section of the Association of Lunar and Planetary Observers (A.L.P.O) and the Terrestrial Planets Section of the British Astronomical Association (B.A.A.). Information for observing Mars during a typical apparition is presented in a separate report titled, General Information for Apparitions of Mars. Also, you can find gobs of information at this site.
With the advent of modern CCD camera technology the amateur can produce useful images of Mars when it is as small as 3.5 arcsec . Early in an apparition, Mars rises in the east or morning sky and sets with the rotation of the Earth in the western or evening sky. During the past few apparitions (2018-2025), observers began to take CCD images when Mars was only 30 degrees away from the Sun. Since Mars was only a visual magnitude of ~1.8 then the planet would have been difficult to locate bright twilight hours.
In the pre-apparition reports the observer will find the motion of Mars in our sky, the characteristics for that particular apparition, information pertaining to the polar cap(s) and any special events that may be seen during that particular apparition. As usual a calendar of events will be included with each report that contains cardinal dates for seasonal activity and orbital information of Mars.
MOTION OF MARS IN OUR SKY
As a general rule, an "apparition" begins when a planet emerges from the glare of the Sun shortly after conjunction. Mars will be in conjunction with the Sun on January 09, 2026 at 09:59UT (203.8° Ls); however, it will not be safe to observe Mars until after March 03, 2026 when it is at least 12 degrees away from the glare of the Sun. By November 20, 2026, a 0.6 visual magnitude Mars is seen rising early in the morning sky in the constellation Leo, it will be at western quadrature and the phase or terminator will be 38°.
The apparent declination of Mars begins at -23° in early January 2026 and continues to climb northward until opposition. This is good news for those observing in the Northern Hemispheres because Mars will be seen high in their sky. Mars will be below the celestial equator until April 13, 2026.
NOTE: The Solar Elongation for Mars is the angle between the lines of sight from Earth to the Sun and from Earth to Mars. When these lines of sight form a right triangle then Mars is at quadrature (eastern or western). For detailed definitions and graphics for the motion of Mars in our sky see these excellent web sites: Planetary Aspects and Elongations and Configurations.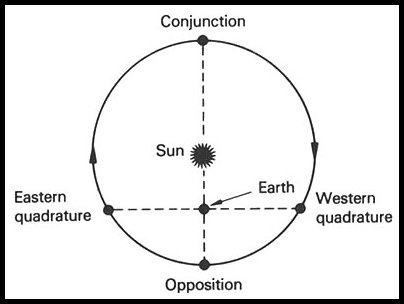
Figure 1. A heliographic chart of the orbits of Mars and the Earth showing the relative positions of both planets. Quadrature is when Mars is directly east or west of Earth as shown.
The 2026-2027 Mars apparition begins retrogression, or retrograde motion against the background stars just over a year after conjunction from January 10, 2027 (47.5° Ls) through April 01, 2027 (83° Ls). Each night for this brief period before, during and after opposition the Red Planet will appear to move backwards toward the western sky from the constellation in Leo. Since the Martian year is about 687 Earth days long -- nearly twice as long as ours, the Martian seasons are similarly extended. While the Earth’s seasons are nearly equal in duration, the Martian seasons can vary by as much as 52 days from each other due to that planet’s greater orbital eccentricity (see Figure 2).
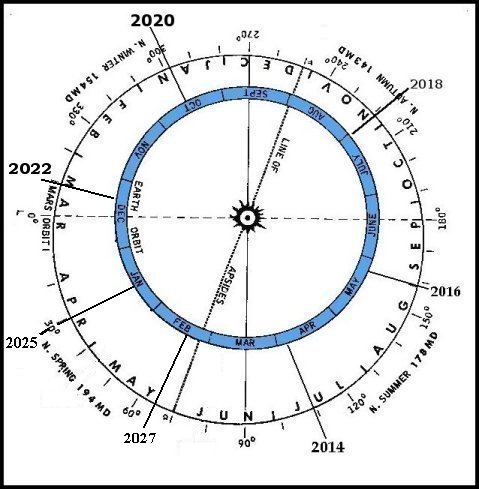
Figure 2. A heliographic chart of the orbits of Mars and the Earth showing the relative seasons of both planets in the planetocentric longitude system Ls. Graphic Ephemeris for the 2027 Aphelic Apparition of Mars. Original graph prepared by C.F. Capen and modified by J.D. Beish.
2027 APPARITION CHARACTERISTICS
Another general rule for predicting oppositions of Mars is from the following: the planet has an approximate 15.8-year periodic opposition cycle, which consists of three or four Aphelic oppositions and three consecutive Perihelic oppositions. Perihelic oppositions are also called "favorable" because the Earth and Mars come closest to each other on those occasions. We sometimes refer to this as the seven Martian synodic periods. This cycle is repeated every 79 years (± 4 to 5 days) and, if one were to live long enough, one would see this cycle nearly replicated in approximately 284 years. The 2027 Mars apparition is considered Aphelic because the orbital longitude at opposition will be only 4.5° from the aphelion longitude 70° Ls.
NOTE: Ls is the planetocentric longitude of the Sun along the ecliptic of Mars’ sky. 0° Ls is defined as that point where the Sun crosses the Martian celestial equator from south to north, that is the planet’s northern hemisphere vernal equinox. The other Ls values that define the beginnings of Martian northern hemisphere seasons are: summer, 90° Ls; autumn, 180° Ls; and winter, 270° Ls. For Mars’ southern hemisphere these values represent the opposite seasons. Distance (A.U.) - Distance from Earth to Mars in astronomical units, where one (1) A.U. equals 92,955,807.267 miles or 149,597,870.691 km.
Opposition occurs
14.3 months after conjunction, when Mars is on the opposite
side of the Earth from the Sun. At that time, the two planets
will lie nearly in a straight line with respect to the Sun, or
five weeks after that retrogression begins. Opposition will occur
at 1545 UT on February 19, 2027 (65.4° Ls), with an apparent
planetary disk diameter of 13.8 arcsec. Mars will remain visible
for a year after opposition and then become lost in the glare of
the Sun again (May 13, 2028) as it approaches the next
conjunction March 21, 2028 at 0116 UT (275.6° Ls). The cycle is
complete in 780 Earth days.
Closest approach ooccurs at 0014 UT on February 20 (65.5° Ls) with an
apparent planetary disk diameter of 13.8’’ at a
distance of 0.6779190 astronomical units (AU) or 63,016,511 miles
(101,415,244 km). During closest approach in 2027 the apparent
diameter of Mars will be 0.8 arcsec smaller than it was at the
same period in 2025 and it will be 9.4 degrees lower in the sky -
favorably placed for observing the Red Planet. [NOTE: one
(1) A.U. equals 92,955,807.267 miles or 149,597,870.691 km]. It
should also be noted that closest approach between Earth and Mars
is not necessarily coincident with the time of opposition but
varies by as much as two weeks.

Figure 3. A simulated view of the appearance of Mars during opposition at 1545 UT on February 19, 2027 (65.4° Ls, CM 34°)
The observable disk diameter of Mars will be greater than 6
arcsec from October 14, 2026 [19.2° δ] (6.7°
Ls) and will not fall below this value until July 01, 2027
[3.7° d]
(124.1° Ls), lasting nearly 8.7 months or 117 degrees
Ls. This apparition will follow a similar profile to the
2012 apparition of Mars. Imaging by CCD devices may begin with a
disk diameter of 4 arcsec or more, commencing on or about
February 09, 2026.
The Sub-Earth (De) and
Sub-Solar (Ds) points are graphically
represented in Figures 4 and 5. The 2026-2027
Ephemeris of Mars is tabulated on Internet in this web site.
A glossary of Terms appears at the end of this table.

Figure 4. As it approaches Earth, it will swell from a small apparent disk of 6" in October14, 2026 to a maximum diameter on July 01, 2027, and then shrink as it moves away. Closest approach occurs on February 20 (65.5° Ls). Opposition on February 19, 2027 (65.4° Ls). From October 2026 through June 29 are the prime observing months. Images shows at 0h UT.
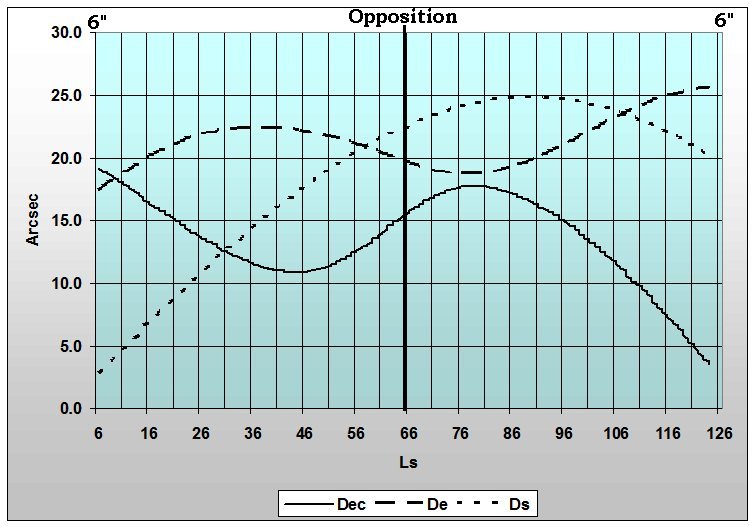
Figure 5. Graphic Ephemeris of Mars during the 2026-2027 apparition from October 14, 2026 through July 01, 2027. Opposition (65.5° Ls) and 6 arcsec apparent diameter range arc indicated. Plot illustrates the Declination (solid line), the latitude of the Sub-Earth point (De) or the apparent tilt (dashed line) in areocentric degrees, and the latitude of the Sub-Solar point (dotted line) in areocentric degrees. The areocentric longitude (Ls) of the Sun, shown along the bottom edge of the graph defines the Martian seasonal date. The value of Ls is 0° at the vernal equinox of the northern hemisphere, 70° when Mars is at aphelion, and 90° at the summer solstice of the northern hemisphere 250° when Mars is at perihelion, and 180° is northern autumn.
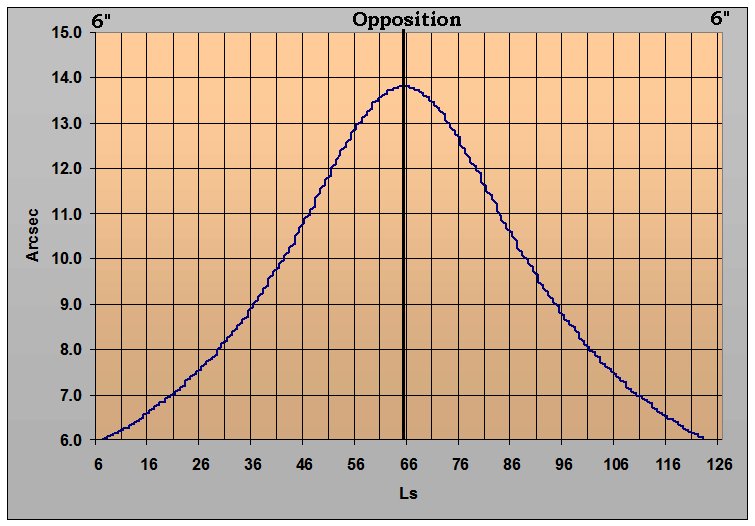
Figure 6. Graphic Ephemeris of Mars from October 14, 2026 through July 01, 2027. Opposition (65.5° Ls) and 6 arcsec apparent diameter range arc indicated. Plot illustrates the apparent diameter of Mars in seconds of arc. The areocentric longitude (Ls) of the Sun, shown along the bottom edge of the graph defines the Martian seasonal date.
THE NORTH
AND SOUTH POLAR REGIONS
Astronomers will have an excellent view of the prominent north polar cap during most of the next apparition because it will be tilted earthward during the entire apparition. The terminator shadow will cover part of polar cap until late-November 2026 when the cap will become completely sunlit. For more detailed information on the For more detailed information on the north polar cap click to this web site.
DUST STORMS
Observations of Mars indicate that dust storms occur around the time of southern summer solstice, soon after Mars reaches perihelion. However, accurate predictions are nearly impossible to make because of the complexities and unknown variables. When a great dust storm reaches maturity, Mars’ disk appears bright orange and Mars’ surface features are obscured. For more detailed information on Martian dust storms on this web site Martian dust storms
While Mars will be too close to the Sun the Martian dusty season should begin about the third week in January (210° Ls) throughout the first week of August 2026 (330° Ls). The highest probability of dust storms occurring will be on or about March 05, 2026 (241° Ls) and a sensitive area for the development of dust storms is in northwest Hellas. Also, dust clouds and storms have been observed during northern summer (105° Ls) and be on the watch on or about May 20, 2027.
Another sensitive period following the
"procurer" storm season will come in the middle of July
2026 (315° Ls) when observers should be alert for dust clouds in
the northeast Hellas Basin, the Serpentis-Noachis region, and the
Solis Lacus region.
CALENDAR OF EVENTS -- MARS, 2026-2027
|
DATE |
PHYSICAL |
REMARKS |
|
2026 Jan 09 |
Ls 203° |
Conjunction. Mars is behind the Sun ~2.404 AU. |
|
2026 Mar 24 |
Ls 250° |
Mars at Perihelion. SPC in rapid retreat. Novus Mons smaller. Dust clouds expected over Serpentis-Hellaspontus (Ls 250° - 270). Syrtis Major beginning to narrow. Frost in bright deserts? Orographic clouds (W-clouds) possible. Elysium and Arisa Mons bright? Note: Several "planet-encircling dust storms have been reported during this season. High probability for dust clouds at 255° Ls. SPC ~ 24° ±4° |
|
2026 Apr 25 |
Ls 270° |
Solstice - Northern Winter/Southern Summer. W-clouds present? NPH extends 50° N? Decreased number of White clouds. "Syrtis Blue Cloud"? White areas in deserts? Dust clouds in south until 270° Ls? Watch for planetary system clouds bands. Orographic cloud over Arsia Mons? Syrtis Major is narrow. SPC ~17° ±2° |
|
2026 Sep 30 |
Ls 0° |
Equinox - Northern Spring/Southern Autumn North Polar Hood (NPH) breaking up, North Polar Cap (NPC) should be exposed. ("Areo-" is a prefix often employed when referring to Mars or "Ares.") |
|
2026 Oct 14 |
Ls 0.8° |
Apparition begins for observers using 4-inch to 8-inch apertures telescopes and up. Begin low-resolution CCD imaging. Views of surface details not well defined. White areas? Orographic clouds over the Tharsis volcanoes. W-Cloud? Orographic cloud over Arsia Mons? SPC very small, difficult to see. Edom bright? Is SPC remnant visible in mid-summer? High probability of dusty storm at 315° Ls. Orographic cloud over Arsia Mons? Topographic cloud over Libya? |
|
2026 Nov 19 |
Ls 23.9° |
Western Quadrature. NPC nearly static or entering erratic retreat, hood dissipating? Orographic cloud over Apollinaris Petera? Limb clouds and hazes should start to increase. Dust clouds in NPR? |
|
2026 Dec 02 |
Ls 29.5° |
Limb clouds and hazes should start to increase. Limb arcs increasing in frequency or intensity? Arctic hazes and clouds? Dust clouds in NPR? |
|
2027 Jan 10 |
Ls 47.1°
|
Retrogression Begins. Few clouds. Limb arcs increasing in frequency or intensity? Arctic hazes and clouds? Dust clouds in NPR? Continue NPC measurements. Is North Cap fairly static or entering rapid retreat phase. South polar regions becoming difficult to observe. Any signs of South Polar Hood (SPH)? NPC ~50-47 ±6 |
|
2027 Feb 19 |
Ls 65.1° |
Mars at Opposition Micrometer measurements of NPC possible. Watch for "Aphelic Chill" in North Polar region (NPR) - (usually between 60° and 70° Ls) and possible halt in thawing of NPC. Views of surface details well defined. Rima Tenuis may appear (140° and 320° areographic meridians). Cloud activity in north increasing? |
|
2027 Feb 20 |
Ls 65.5° |
Mars at Closest Approach . Watch for "Aphelic Chill" in NPR (usually between 60° and 70° Ls). Antarctic hazes, hood. South polar regions becoming difficult to observe. Any signs of SPH? Cloud activity increases. Are limb arcs increasing in frequency, intensity? |
|
2027 Mar 02 |
Ls 70° |
Mars at Aphelion. Is North Cap fairly static or entering rapid retreat phase. Watch for "Aphelic Chill" in NPR (usually between 60° and 70° Ls). NPC Rima Tenuis may appear. Antarctic hazes, hood. South polar regions becoming difficult to observe. Any signs of SPH? Cloud activity increases. Are limb arcs increasing in frequency, intensity? (NPC W ~31° ±3°). |
|
2025 Feb 24 |
Ls 83.0° |
Retrogression Ends. NPC in rapid retreat? Are limb arcs increasing in frequency, intensity. Antarctic hazes/hood. Cloud activity increases. "Aphelic Chill" in NPR should be ended. |
|
2027 Apr 15 |
Ls 89.2° |
Is North Cap fairly static or entering rapid retreat phase. South polar regions becoming difficult to observe. Any signs of SPH? Discrete clouds? Increasing ice-fogs and clouds? Watch for dust clouds and possible dust storms. (NPC W ~15° ±3°). |
|
2027 Apr 17 |
Ls 90° |
Solstice - Northern Summer/Southern Winter. Orographic clouds over the Tharsis volcanoes - W-Cloud? Local seasonal clouds should wrap around Syrtis Major and be prominent in Lybia. Hellas white cloud and Ice-fog activity? Discrete clouds? NPC remnant? Lemuria (210° W, 82° N) detached from NPC? Any other detachments (projections at 135° W and 290° W) near NPC remnant? NPC ~20 ±4.; |
|
2027 May 12 |
Ls 101.2° |
Is North Cap fairly static or still in retreat phase? South polar regions becoming difficult to observe. Any signs of SPH? Discrete clouds? Increasing ice-fogs and clouds? Dust at 105° Ls? |
|
2027 May 26 |
Ls 107° |
Eastern Quadrature. . NPC still retreating? Are limb arcs increasing in frequency, intensity? Antarctic hazes, hood? Cloud activity high? Tempe-Arcadia-Tharsis-Amazonis regions bright in a pattern appearing as the "domino effect." Discrete clouds? ; |
|
2027 Jun 29 |
Ls 123.2° |
Is Mare Acidalium broad and dark? Bright spots in Tempe-Arcadia-Tharsis-Amazoins? "Domino effect" appears around 120° - 125° Ls. Topographic clouds increase. |
|
2028 Mar 21 |
Ls 276° |
Conjunction. Mars is behind the Sun ~2.388AU. |